What Is THC?
Tetrahydrocannabinol, or THC, is the compound in cannabis that’s primarily responsible for its intoxicating, psychoactive effects. Discover how THC works, potential effects, tips for selecting products and more.
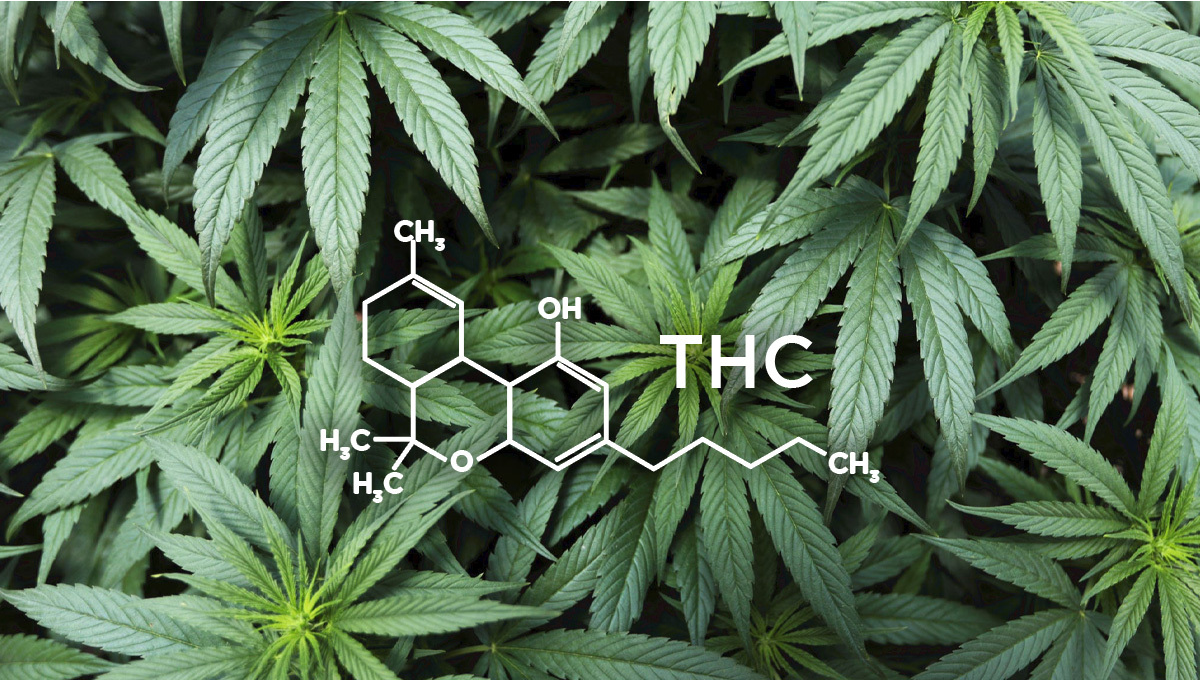
Approximately 100 naturally occurring chemical compounds, known as cannabinoids, are present in the cannabis plant. Among these, THC (scientifically named delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol) is primarily responsible for the psychoactive and intoxicating effects of cannabis consumption. Keep reading to understand how THC operates in the body, its potential effects (both positive and negative), how to select products based on potency, and how THC compares to CBD.
How THC Works
As a cannabinoid, THC interacts with the body’s endocannabinoid system (ECS). Studies suggest that this system plays a role in regulating stress recovery, protecting the nervous system, activating the immune system response, and maintaining overall health and stability (homeostatic balance).
The ECS consists of two components:
-
Endocannabinoids – cannabinoids produced naturally by the body
-
Cannabinoid receptors – present in nearly every part of the central nervous system, brain, and various other body areas, including the immune system
Natural endocannabinoids fit into receptors like a key in a lock, facilitating communication between cells. THC, as a cannabinoid, operates similarly by temporarily replacing endocannabinoids and binding to receptors, but with different effects.
Potential Effects of THC
Short-term effects of consuming cannabis, which may be attributed to THC, include:
-
Heightened feelings of relaxation, calm, and euphoria
-
Sleepiness and fatigue
-
Time distortion and changes in perception
-
Impaired ability to remember, concentrate, and pay attention
-
Anxiety and panic
-
Increased appetite
-
Reduced reaction time and loss of coordination
-
Chest pain and changes in heartbeat
-
Seizures
Cannabis products containing THC can have various short- and long-term effects on the mind and body. Unpleasant or undesired effects are possible, especially with overconsumption, though there have been no documented cases of death due to cannabis overconsumption.
For some individuals, regular cannabis use poses the risk of long-term effects and conditions, such as impaired cognitive functions, cannabis use disorder, psychosis, and schizophrenia.
Personal Factors and THC
The effects of THC vary among individuals, influenced by factors like THC potency, method of consumption, and amount consumed. Other personal factors include:
-
Age, sex, and weight
-
Health history and existing mental health conditions
-
Genetic makeup
-
Previous experience with cannabis and frequency of use
-
Personality and current mood
-
Metabolism and recent food consumption
These factors, along with consumption details, affect how long THC remains active in the body. While effects may take up to 24 hours to disappear, THC can be detected in the bloodstream for seven days or more.
Understanding THC Concentration
Concentration or potency refers to the amount of THC in a cannabis product. Cannabis, in its fresh form, contains tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA), the non-active version of THC. Decarboxylation, achieved through heating, drying, or curing, activates THC.
THC content is listed on packaging, expressed in milligrams per package, gram, or unit. It’s presented as “THC,” the amount when purchased, and “Total THC,” the content when heated.
Types of THC Products
Various cannabis products contain THC in different potencies, with the method of consumption influencing the experience. Some products and their potential potency include:
-
Dried Flower: Inhalation (up to >20% THC)
-
Edibles: Ingestion (up to 20 mg THC per package)
-
Concentrates: Inhalation (up to 1,000 mg THC per package)
-
Extracts: Oral absorption (up to 1,000 mg THC per package)
-
Topicals: Topical application (up to 1,000 mg THC per package, rarely psychoactive)
Choosing Cannabis Products Based on THC Potency
Consider the following when buying THC products:
-
Small amounts may produce pleasant effects, while large amounts may lead to unpleasant or harmful effects.
-
Potency can vary between batches, so check labels for accurate THC content.
-
Choose products with low THC concentration or at least a 1:1 ratio of THC to CBD.
-
Start with a low dose and increase gradually, allowing time to feel effects before consuming more.
THC vs. CBD: What’s the Difference?
THC and CBD affect the body differently:
-
THC produces intoxicating effects, while CBD does not.
-
CBD enhances the production of endocannabinoids rather than replacing them like THC.
-
CBD may reduce some psychoactive effects of THC when present in equal or greater amounts.

