The Endocannabinoid System: What It Is and How It Works
Curious about what happens in your body when you consume cannabis? Let’s delve into how the endocannabinoid system operates, how plant cannabinoids interact with it, and how these processes can influence the effects of cannabis.
What is the endocannabinoid system?
The endocannabinoid system is an intricate cell-signalling system crucial for regulating and balancing various processes in the body. Given its influence, it’s no surprise that cannabis can produce a broad range of effects.
Humans and cannabis plants share chemical compounds in their systems called cannabinoids. In humans, they’re known as endocannabinoids, while in plants, they’re termed phytocannabinoids. The cannabis plant contains numerous cannabinoids, with tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) being the most studied.
THC influences how your brain and body respond to cannabis consumption, including the majority of the psychoactive effects or the “high” you may experience. In contrast, CBD is believed to be non-intoxicating. Researchers are exploring how CBD collaborates with THC and other minor cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids in cannabis to produce effects collectively known as the “entourage effect.”
How does the endocannabinoid system work?
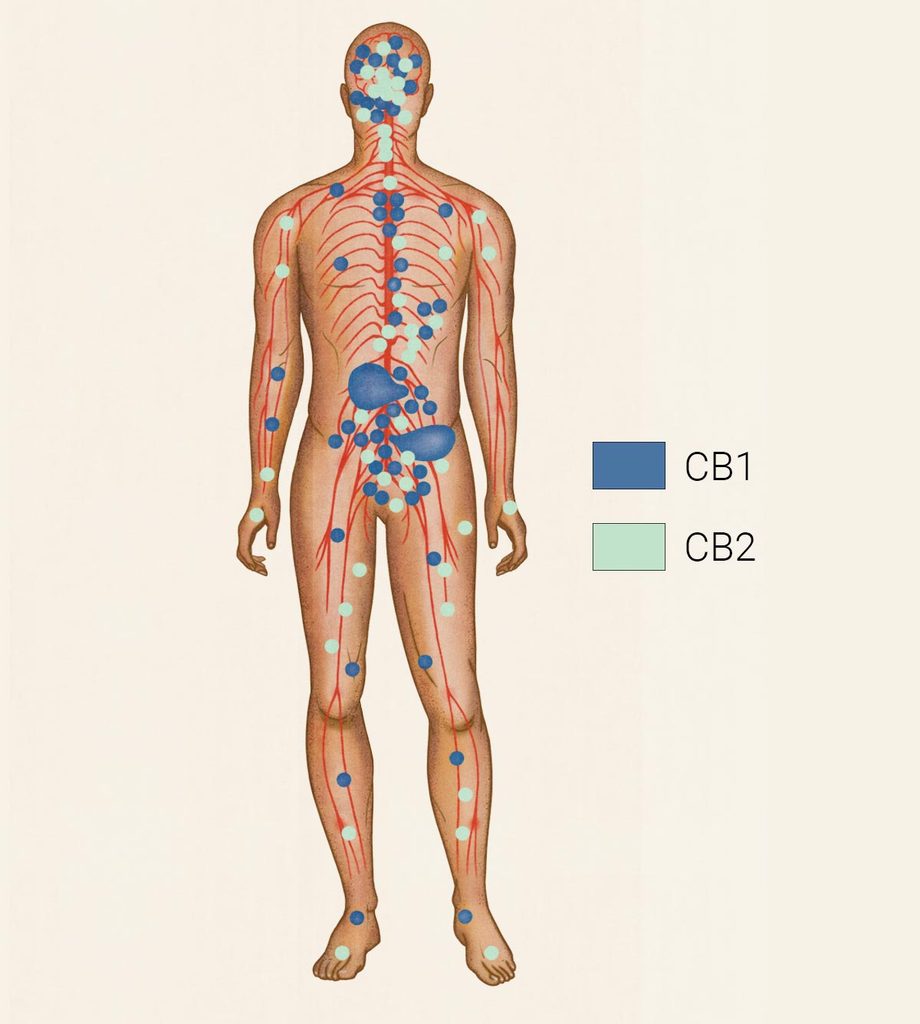
Humans internally produce cannabinoids through the endocannabinoid system, which plays a role in regulating stress recovery, nervous system protection, immune system response, and overall homeostatic balance — our optimal health function and stability. Endocannabinoids bind to cannabinoid receptors all over the body and brain to help regulate these functions.
The endocannabinoid system comprises three main components: endocannabinoids, cannabinoid receptors, and enzymes that process and break down endocannabinoids.
Endocannabinoids:
-
Anandamide (AEA or arachidonoylethanolamide)
-
2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG)
Cannabinoid receptors:
-
CB1 receptors (mostly in the central nervous system)
-
CB2 receptors (primarily in the immune system and certain organs)
Enzymes:
-
Fatty acid amide hydrolase (breaks down AEA)
-
Monoacylglycerol acid lipase (breaks down 2-AG)
What does the ECS do?
The endocannabinoid system goes beyond processing cannabis. Research indicates that it helps the body maintain balance or homeostasis in response to environmental changes, such as stress, injury, or disease. It regulates various bodily functions, including motor control, sleep, appetite, mood, pain control, inflammation, immune responses, and brain function such as learning and memory.

